Officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, this beautiful country is nestled between China to the North and India to the South, East and West. Known for its natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and the majestic Himalayas, Nepal holds a unique place in the world.
🏔️ Geography
-
Area: Approximately 147,516 square kilometers
-
Landscape: Nepal is geographically divided into three main regions:
-
Himalayan Region (north) – Includes Mount Everest (8,848.86 m), the world’s highest peak
-
Hilly Region (middle) – Includes major cities like Kathmandu and Pokhara
-
Terai Region (south) – Flat, fertile plains; agricultural heartland
-
-
Climate: Ranges from alpine in the north to subtropical in the south
👥 Population
-
Total Population (2024 est.): Around 30 million
-
Ethnic Groups: Highly diverse, with over 125 ethnic groups and over 100 languages
-
Major groups: Chhetri, Brahmin, Magar, Tharu, Tamang, Newar, Gurung, Rai, Limbu, Sherpa
-
-
Languages:
-
Official language: Nepali
-
Many regional and ethnic languages are also spoken
-
-
Major Religions:
-
Hinduism (about 81%)
-
Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, and others
-
🏛️ A Brief History
-
Ancient Nepal: Historically part of various small kingdoms; the Licchavi and Malla dynasties were prominent.
-
Unification: In the 18th century, King Prithvi Narayan Shah unified the small kingdoms into modern Nepal.
-
Never Colonized: Unlike many South Asian nations, Nepal was never colonized, though it maintained a complex relationship with British India.
-
Democracy & Monarchy:
-
Nepal was a monarchy for centuries.
-
In 2008, after a decade-long civil conflict (Maoist insurgency), Nepal abolished the monarchy and became a Federal Democratic Republic.
-
🏙️ Major Cities
-
Kathmandu (Capital and largest city)
-
Pokhara – Tourism and adventure hub
-
Biratnagar, Birgunj, Butwal, Dhangadhi, Nepalgunj
🌐 Political System
-
Government: Federal parliamentary republic
-
President: Head of state
-
Prime Minister: Head of government
-
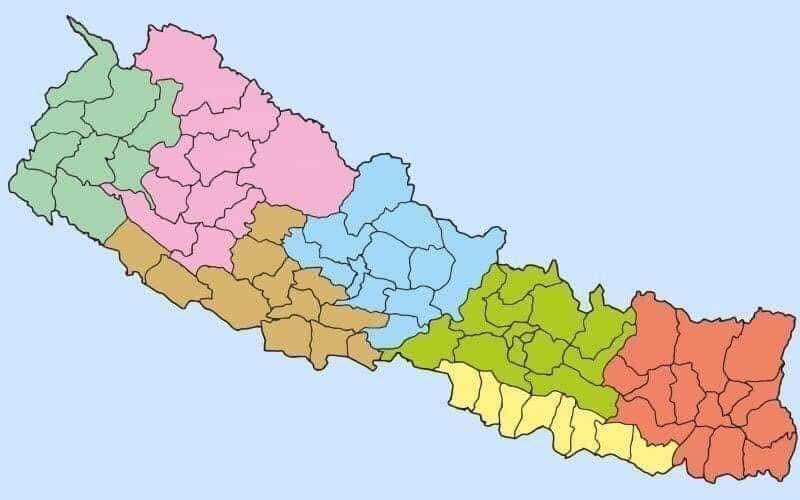
Divided into 7 provinces and 77 districts
🌄 Tourism & Culture
-
Mount Everest, Lumbini (Birthplace of Lord Buddha), Pashupatinath Temple, Boudhanath Stupa, and Chitwan National Park
-
Rich in festivals, handicrafts, dance, and traditional music
-
Nepal is a popular destination for trekking, mountaineering, and spiritual tourism
🛠️ Economy
-
Based on agriculture, remittances, tourism, and hydropower
-
Nepal is one of the least developed countries, but has great potential in renewable energy, eco-tourism, and youth entrepreneurship.






